Structure & Function
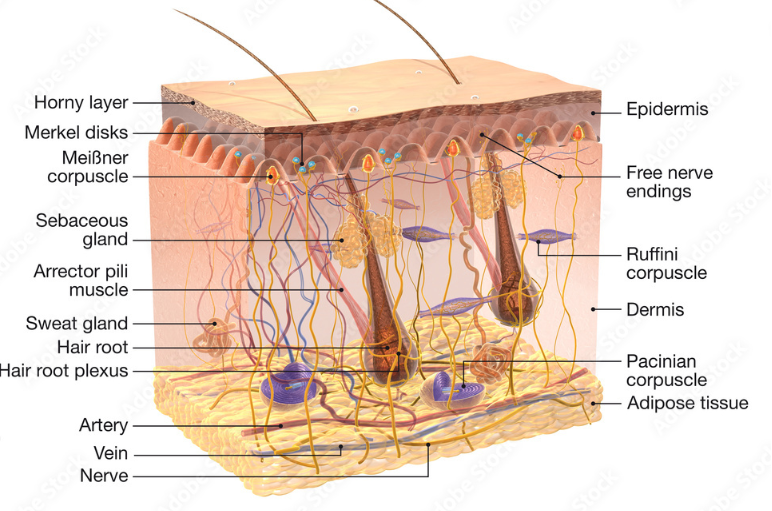
The integumentary system is the body’s outer protective covering.
It is composed of:
-
Skin — the main organ, consisting of:
-
Epidermis: the outermost layer made mostly of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium.
-
Dermis: the thicker inner layer containing connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves, glands, and hair follicles.
-
(Sometimes the hypodermis or subcutaneous layer is included; it lies beneath the skin and contains fat and connective tissue.)
-
- Accessory structures (skin appendages):
-
Hair — provides protection and helps with temperature regulation.
-
Nails — protect the fingertips and aid in grasping.
-
Sweat glands (sudoriferous glands) — help regulate body temperature by secreting sweat.
-
Sebaceous glands — produce sebum (oil) that lubricates and waterproofs the skin and hair.
-
- Associated sensory receptors — detect touch, pressure, pain, and temperature.
The physiology of the integumentary system centers on maintaining barrier integrity, thermoregulation, sensation, immunity, metabolism, and repair.